As we navigate the vast landscape of the internet, it indeed serves as a treasure trove of information, connecting us with knowledge, entertainment, and social connections.
However, beneath the surface lies a lurking danger in the form of cyber threats, orchestrated by individuals with malicious intent, commonly known as hackers. These individuals can compromise our digital security, stealing sensitive information and exploiting vulnerabilities.
It’s essential to recognize the duality within the hacking community. “White Hat” hackers are ethical hackers who assist companies and organizations in identifying and fixing security flaws. On the other hand, “Black Hat” hackers engage in malicious activities, orchestrating cyber attacks, writing malware, and breaching data.
The year 2018 witnessed significant cyber threats and attacks, with hackers deploying sophisticated techniques, including the creation of new malware to infiltrate systems. As we delve deeper into the digital realm, understanding these threats becomes crucial for safeguarding our online presence and personal information.
Based on the records conducted by breachlevelindex.com all data records that were lost or stolen from 2013 to 2019 reached about 14,717,618,286 and still growing– malware and black hats are a part of this data breach.
- 1. Ransomware
- Types of Ransomware
- 2. Trojan Horse
- Basic History Of Trojan
- Most Destructive Trojans Ever Created
- I LOVE YOU
- Zeus or Zbot
- Basic Information Of Cryptocurrencies
- Crypto Jacking Become Lucrative
- Two Types of Cryptojacking
- How Can CrytoJacking Affect your Device?
- 4. Phishing
- What Are Kinds Of Phishing?
- Basic History Of Phishing
- The First Phishing Attacked on the Internet
- 5. Worms
- What is a Computer worm?
- A Basic History Of Worm
- Worm Effects On a Device/Computer
- How Can you get Infected by Worm Malware?
- 6. Virus
- 7. Spyware

No. of data records since 2013 up to this date Screenshot via breachlevelindex.com
What Is An Online Data Breach?
An online data breach refers to the unauthorized access, disclosure, or acquisition of sensitive information stored digitally.
Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in a system’s security to gain access to databases, networks, or cloud storage, compromising personal, financial, or corporate data.
These breaches can result from various cyber-attacks, such as hacking, phishing, or malware infections.
Once inside, attackers may steal, manipulate, or sell the acquired data, leading to identity theft, financial losses, or reputational damage for individuals and organizations. Preventing online data breaches involves robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
Social Media are Prone to Online Data breach
Data breaches have become a prevalent cyber threat, and social media platforms, in particular, are increasingly vulnerable.
According to breachlevelindex.com, a significant 56.18% of data breaches originate from social media platforms. These breaches often lead to identity theft, a malicious act where personal information is exploited for financial gain.
Identity thieves capitalize on the data they acquire from social media breaches by selling it in underground marketplaces.
As the number of social media users continues to rise, it becomes imperative for individuals to be aware of the potential threats associated with these platforms. Taking measures to enhance online security and privacy is crucial in mitigating the risks posed by data breaches and identity theft.
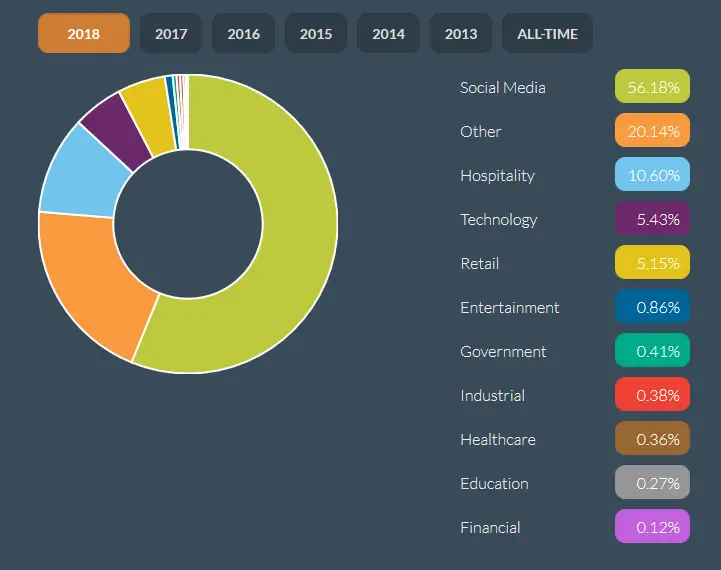
Screenshots via breachlevelindex.com
More and more Malware Each year
The increasing prevalence of Internet of Things (IoT) malware is a cause for concern, as highlighted by a study conducted by McAfee.
In the third quarter alone, there were 45,000 new instances of IoT malware detected. This alarming trend is fueled by the growing number of people gaining access to the internet, coupled with the surge in online transactions.
The broader attack surface created by the expanding IoT landscape poses a significant risk, as cybercriminals find more opportunities to target devices, compromise bank accounts, and access valuable information.
As technology continues to advance, it becomes crucial for users to adopt robust security measures to safeguard their devices and personal data from evolving cyber threats.
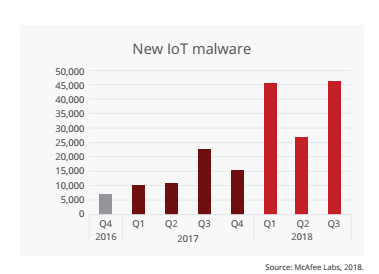
Screenshot via Mcafee Threats reports
There are many kinds of cyber threats like malware on the internet that can steal pieces of information and bring chaos to our devices.
What Are the Types Of Malware?
To protect ourselves from cyber threats, malware, or hackers, we must be fully aware of the possible threats that we might face on the internet.
Having basic information about different kinds of cyber threats, such as malware, hackers, and other internet thieves, and understanding how to prevent them are our greatest weapons. Why?
Because it’s simple: internet thieves cannot operate without you. If you know what you are doing and know how to prevent them, you can protect yourself from possible cyber threats online.
Malware

What is Malware And Why Is It One of the Cyber Threats That We Might Encounter?
Some other says the malware is derived from the French word malaise or sickness. but actually, malware is just short-term “malicious software”.
It simply means that any software or program with malicious intent that can gain unauthorized access is called malware.
Types Of Malware
1. Ransomware
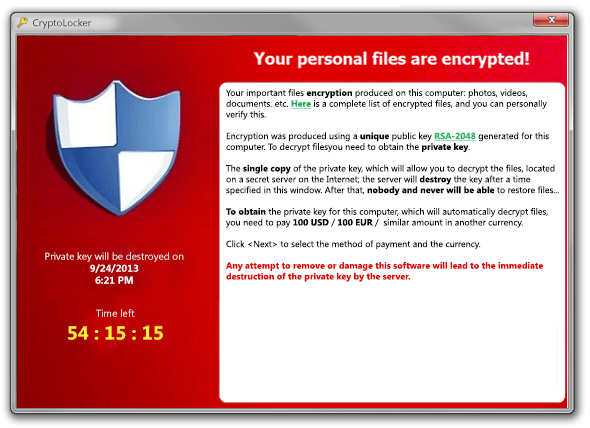
Ransomware pop-ups in infected PC.Screenshot via securingtomorrow.mcafee.com
Ransomware is a type of malware that typically encrypts and locks files or even entire devices of its victims.
When ransomware infects our PC or devices, it demands ransom money in exchange for an encryption key. The authors of ransomware will force victims to pay, and if the victim refuses to pay the ransom, they may delete all valuable files, or worse, they can even destroy the device.
Types of Ransomware
Ransomware has been notorious for many years and stands out as one of the most severe cyber threats that individuals may encounter. There are two primary types of ransomware: CryptoLocker and Locker ransomware.
CryptoLocker ransomware operates by encrypting personal data and files, effectively blocking user access to crucial information.
On the other hand, Locker ransomware takes a different approach by encrypting the entire computer, thereby preventing the user from accessing their computer or device.
Basic History And Information About Ransomware
The first recorded ransomware attack dates back to 1989 when a biologist named Joseph L. Popp, a Harvard Ph.D. in biology, created the initial ransomware. At the World Health Organization International AIDS conference, Popp distributed 20,000 floppy disks labeled “AIDS Information.”
Unbeknownst to the delegates, these disks were infected with a Trojan. Once the computer reached 90 boots, the Trojan would activate, hiding and encrypting directories. Subsequently, victims received a ransom demand of $189 to regain access to their files. The ransom amount was instructed to be sent to a P.O. box in Panama.

The original messages of the first ransomware were created by Joseph L. Popp. Screenshots via www.knowbe4.com.
In 2005, hackers revived ransomware after recognizing its significant potential for monetization. Presently, numerous types of ransomware evoke terror globally. Among them, the two most widely known and impactful are CryptoLocker and WannaCry.
According to Datto, CryptoLocker ransomware accounts for 71% of ransomware attacks, while WannaCry ransomware is responsible for 50% of these incidents.
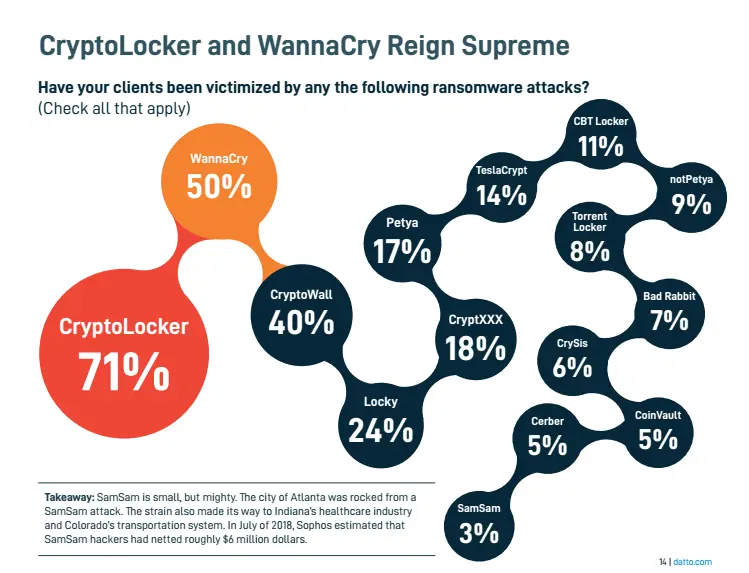
CryptoLocker and WannaCry have the biggest internet safety threats in Ransomware history. Screenshots via Datto.com
As ransomware is one of the biggest Cyber threats, they have their prime targets, and below is the list of Industries targeted by ransomware attacks.
Industries Targeted by Ransomware
Construction/ manufacturing companies 38%
Professional service 35%
Finance/ Insurance 27%
Healthcare 25%
Legal 21%
Non-profit 20%
Real Estate 15%
Retail 15%
Education 11%
Consumer Products 10%
Travel/ Transportation 10%
Architecture/Design 10%
Government 8%
Os targeted by ransomware
Windows 99%
macOS 9%
Android 8%
iOs 5%
2. Trojan Horse

Have you heard about the story of the wooden horse used by the Greeks to defeat the Trojans?
During the war, the Trojan army believed that the Wooden Horse was a symbol of surrender. They brought the horse inside their walls, unaware that enemy soldiers were hiding within. The Trojans were subsequently caught off guard by the hidden soldiers, leading to their defeat.
In computing, a Trojan horse is a type of program that employs deception and social engineering to trick users, disguising itself as legitimate software. It is termed a trojan due to its deceptive nature, and many individuals fall victim to these cyber threats.
Types of Trojans
There are various types of Trojans found on the internet, and here are some examples that individuals may encounter:
- Downloader Trojans: These Trojans download and install other malicious programs on victims’ devices, such as keyloggers or ransomware.
- Spyware: This type of Trojan is used by cybercriminals to spy on your device, enabling them to steal sensitive data like credit card information.
- Backdoor Trojans: Hackers utilize these Trojans to create backdoors, gaining unauthorized access to your device and carrying out malicious activities.
- Zombifying Trojans: Hackers deploy thee Trojans to infect and control multiple devices. Under the hackers’ control, they can create an army of computers to be used in performing distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
- Trojan-FakeAV: This Trojan poses as an anti-virus program, reporting non-existent threats to the user and extorting payments.
- Trojan-MailFinder: This Trojan can harvest email addresses from the infected device.
- Trojan-Arcbombs: Among the most dangerous Trojans, designed to freeze or slow performance or flood the disk with a large amount of empty data, posing threats to files and mail servers. Arcbombs can potentially crash servers.
Basic History Of Trojan
In 1975, the first Trojan was created by John Walker, and it was named ANIMALS.
The program engaged users by asking a series of questions to guess the animals they were thinking of. However, behind the scenes, the program surreptitiously copied itself into directories accessible to other users. While the game itself was not harmful and intended as a prank, its ability to spread throughout the entire computer marked it as the first-ever Trojan created.
Most Destructive Trojans Ever Created
I LOVE YOU
In the year 2000, the internet witnessed havoc when the Trojan known as I LOVE YOU was unleashed.
Two young programmers, Reonel Ramones and Onel de Guzman, released this destructive Trojan into the wild. Disguised as a love letter, the Trojan spread through emails bearing the subject line “I LOVE YOU.”
Innocent victims, driven by curiosity, would click what they believed to be a love letter, only to discover that it was, in fact, a Trojan. Masked as a normal text file, opening the attachment activated the script, causing extensive damage to the local machine. The worm would overwrite random types of files and send a copy of itself to all addresses in the Windows Address Book.
The I LOVE YOU Trojan rapidly spread across Hong Kong, Europe, and the United States. The global damages were estimated at US$5.5-8.7 billion, with an additional US$15 billion required to remove the worm.
Zeus or Zbot
A specific type of Trojan designed to operate on various versions of the Windows operating system is the Zeus Trojan. This malicious software executes criminal tasks, specializing in the theft of banking information through capturing browser keystrokes and logging. Hackers deploy this malware to illicitly obtain credentials, particularly targeting sensitive information related to bank accounts.
In July 2007, Zeus Trojan gained notoriety for pilfering information from the United States Department of Transportation. Subsequently, in June 2009, the security company Prevx revealed that Zeus had compromised over 74,000 FTP accounts.
Zeus employs deceptive tactics, often notifying victims that their device is infected with a virus, which is a mere ruse to trick them into falling for technical support scams and making unnecessary payments.
Trojans, with their stealthy nature, can infiltrate systems by masquerading as legitimate apps or software. It is crucial to exercise caution and remain vigilant against these cyber threats. Beware!
3. Cryptojacking

With the increasing popularity and lucrative potential of cryptocurrencies, hackers have devised new methods to exploit this trend, leading to the emergence of a novel cyber threat known as cryptomining.
Cryptomining, or cryptojacking, has surpassed ransomware as the most prevalent malware in 2018. This type of malware operates covertly, aiming to hijack various devices for a singular purpose — cryptocurrency mining. Unlike ransomware, which focuses on extortion, cryptojacking is designed to remain entirely concealed from users. Victims are often unaware that their devices have been infected, allowing cybercriminals to covertly harness their processing power for cryptocurrency mining. This surreptitious control enables hackers to profit from the computational resources of the infected devices without the knowledge or consent of their owners.
Basic Information Of Cryptocurrencies
The most renowned and presently valued as the highest among all cryptocurrencies is Bitcoin. It was introduced by an unknown individual or a group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, who is also the author of the Bitcoin white paper.
Bitcoin began gaining popularity in 2009. However, during its initial stages, the value of Bitcoin remained relatively low. It wasn’t until 2017 that Bitcoin reached an all-time high value, almost hitting $20,000 per unit.
This surge in Bitcoin’s value in 2017 coincided with a notable increase in the number of Cryptominers. Consequently, more individuals were enticed to invest in cryptocurrencies with the hope of achieving rapid wealth.
Crypto Jacking Become Lucrative
The popularity and high value of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies like Etherium, Moreno, ripple, and other digital money are the rise of a new threat—Cryptojacking.
Two Types of Cryptojacking
File-based Cryptojacking
Hackers employ malware as a means to compromise and take control of your device, utilizing it for cryptocurrency mining. When you inadvertently click on an infected email, a Cryptomining code or script is installed on your device or computer.
Once this code is successfully installed, Cryptojackers seize control, forcing your device to labor in mining their chosen cryptocurrency. This surreptitious exploitation of your device’s processing power enables the hackers to accumulate cryptocurrency without your knowledge or consent.
Drive-by /Browser based Cryptomining
Cryptojackers employ drive-by tactics by embedding JavaScript code into their web pages. This technique allows them to engage in cryptocurrency mining on your machine while you are actively browsing their website.
Drive-by crypto mining itself is not illegal, provided that the owner of the web page is transparent with their visitors. If the website explicitly informs its users that it utilizes their device’s processing power for cryptocurrency mining as an alternative to displaying ads, then the practice is considered legitimate.
The legal concern arises when visitors are not made aware of this mining activity occurring on their devices without their consent. In such cases, where users are kept in the dark about the presence of crypto mining, the practice can be deemed as going against legal standards.
How Can CrytoJacking Affect your Device?
Cryptomining typically involves using specialized machines or devices equipped with high-performance CPUs and GPUs specifically designed for mining operations. However, when your PC or smartphone becomes unwittingly infected by Cryptojacking, and mining occurs secretly without your knowledge, several negative impacts on your devices may emerge.
- Performance Degradation: Cryptomining consumes significant computing resources. As a result, your device’s CPU and GPU may experience a considerable increase in workload, leading to a noticeable slowdown in overall performance. This can manifest as sluggish response times, slower processing of tasks, and potential overheating issues.
- Increased Energy Consumption: Cryptomining is a resource-intensive process that demands a substantial amount of energy. If your device is engaged in mining activities 24/7 without your awareness, it can significantly contribute to higher electricity bills and increased wear and tear on the hardware.
- Reduced Device Lifespan: Continuous and intensive use of the CPU and GPU for mining purposes can lead to accelerated wear and tear on these components. Over time, this may contribute to a reduction in the overall lifespan of your device.
- Security Risks: Cryptojacking often involves the injection of malicious code onto your device. This can open up security vulnerabilities, making your device susceptible to other forms of malware, data breaches, or unauthorized access by external parties.
- Network Congestion: Cryptomining involves the transfer of data between your device and the mining pool. This increased data traffic can lead to network congestion, affecting the performance of other devices connected to the same network.
- Unwanted Expenses: While you may not directly incur costs associated with mining (as the Cryptojackers are utilizing your device’s resources), the increased energy consumption and potential hardware damage could result in higher utility bills or the need for repairs or replacements.
To mitigate the impact of Cryptojacking, it’s essential to employ robust security measures, such as regularly updating your antivirus software, using ad-blockers, and staying informed about potential threats.
- A slowdown in device performance
- Overheating batteries
- The device becomes completely dead and unusable
According to Symantec Threat reports, a device infected by malicious Cryptomining can experience several adverse effects:
- Extended Boot Times: Infected devices may take 5-10 times longer to start up. This prolonged boot time is a result of the increased strain on the system resources due to the Cryptomining process.
- Power Consumption Surge: Cryptomining is known for its significant power consumption. As a consequence, infected devices may contribute to a noticeable increase in monthly electric bills, reflecting the heightened energy usage.
- Processor-Intensive Damage: Cryptomining operations are highly processor-intensive. Continuous mining can lead to accelerated wear and potential damage to the CPU and GPU components of your PC or mobile device.
- Multiple Infections: Cryptomining malware often re-infects the same computer multiple times. This repeated infiltration can compound the negative impact on the device, further slowing down its performance or even causing crashes.
- System Slowdowns and Crashes: The processor-intensive nature of Cryptomining can lead to significant system slowdowns and, in some cases, crashes. This is especially true when the mining process competes for resources with other essential tasks and applications running on the device.
To safeguard against these impacts, it’s crucial to implement robust cybersecurity measures, including regular updates to antivirus software, employing ad-blockers, and staying informed about potential threats. Additionally, practicing safe browsing habits and being cautious about clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files can help prevent Cryptomining infections.
4. Phishing

Phishing is an age-old yet highly effective technique employed by cyber-criminals or hackers to ensnare their victims in a scam. The attackers typically send emails or text messages, claiming that the recipient’s account has been compromised and urging them to re-enter sensitive information such as usernames and login passwords.
For instance, victims may unknowingly sign in to a website that mimics a legitimate platform. By the time they realize the deception, it’s too late—the hackers have gained control of their accounts, pilfered credentials, and potentially stolen their identities.
The above scenario serves as an example of the kind of situation individuals might find themselves in when targeted by a phishing scam. Phishing attempts can originate from emails or text messages, emphasizing the need for extreme caution when clicking on links or providing personal information. It is crucial to adopt a vigilant mindset and remember to “think before we click” to safeguard against falling prey to phishing schemes.
What Are Kinds Of Phishing?
Spear Phishing
These targeted phishing attacks are known as spear phishing, and they focus on specific individuals or organizations. Executing a successful spear phishing campaign requires meticulous pre-attack preparations by the hackers. They scour the internet for information about their targets, gathering details from social media and other online sources. Once armed with the necessary information, the attackers craft highly tailored and authentic-looking attacks.
The distinguishing factor in spear phishing is the level of personalization involved. By leveraging specific details about the target, such as their job title, colleagues, or recent activities, the attackers increase the likelihood of the victim falling for the scam.
This heightened level of sophistication makes spear phishing a potent and deceptive form of cyber-attack, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and cybersecurity awareness at an individual and organizational level.
Whaling
The type of phishing that specifically targets prominent individuals like CEOs and other high-ranking officials is commonly referred to as “whaling” or “big fish” phishing. In this sophisticated form of cyber-attack, the perpetrators set their sights on individuals with significant authority or access to valuable company information.
Whaling attacks often involve careful research and customization to increase their chances of success. Cybercriminals may use tactics similar to spear phishing, tailoring their approach to exploit the specific roles, responsibilities, and personal details of these high-profile targets.
By tricking top-level executives into divulging sensitive credentials or clicking on malicious links, the attackers aim to gain access to confidential company data, financial information, or other valuable assets.
Given the potential impact on organizations and their leadership, defending against whaling attacks requires robust cybersecurity measures, ongoing employee training, and a heightened awareness of the tactics employed by cybercriminals in these targeted phishing schemes.
Clone Phishing
This type of Phishing is often known as “email hijacking” or “email account compromise.” In this scenario, attackers gain unauthorized access to a person’s email account and manipulate the content of previously delivered emails. The attachment or link in the original email is replaced with a malicious substitute that is made to look like a legitimate one. This manipulation can occur without the account owner’s knowledge.
Email hijacking can take various forms, such as re-sending the email with the malicious content or sending an update that appears to be a continuation of the original communication. This technique leverages the trust associated with known email addresses and ongoing conversations to trick recipients into interacting with the compromised content.
To guard against email hijacking and similar phishing tactics, users should enable two-factor authentication, regularly update passwords, and be cautious of unexpected or suspicious emails, even if they appear to come from known contacts. Maintaining a high level of cybersecurity awareness is crucial in preventing falling victim to such deceptive practices.
Basic History Of Phishing
The term “phishing” has its roots in the activities of a group of early tech hackers known as “phreaks.” The phreaks were individuals who experimented with telephone systems, seeking ways to manipulate them, including making long-distance calls without proper authorization. The term “phreaks” is a combination of “phone” and “freaks.”
The concept of phishing was officially introduced in 1987 during a paper and presentation at the International HP Users Group, Interex.
This marked the beginning of the formal recognition of phishing as a distinct method of cyber deception. Since then, phishing has evolved significantly, with cybercriminals continuously refining and adapting their techniques to exploit advancements in technology and human psychology.
The First Phishing Attacked on the Internet
The first known phishing attacks trace back to the 1990s, a period when AOL (America Online) dominated as the leading internet service provider. Given AOL’s popularity, it became a prime target for hackers. These cybercriminals employed various tactics, including software pirates to communicate with each other and launched phishing attacks directly on AOL customers.
As the internet landscape evolved, social networking sites became a new focal point for hackers around the year 2000. These attackers exploited social networks to steal valuable information from victims, and they also targeted online payment platforms like PayPal.
One of the most significant phishing scams occurred in 2017, involving an elaborate scheme that tricked the accounting departments of major tech companies, including Facebook and Google. The hackers successfully convinced these departments to wire a total of $100 million to an overseas bank account controlled by the attackers. This incident highlighted the sophistication and financial implications of large-scale phishing attacks on high-profile targets.
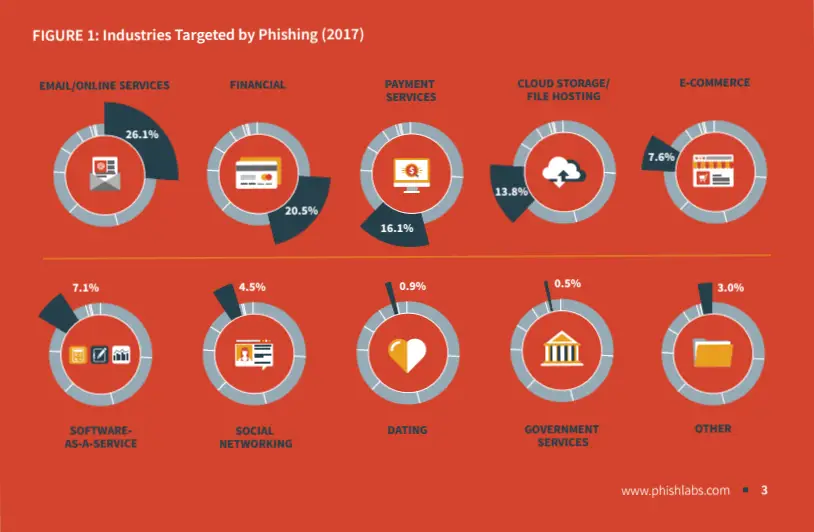
Industries are often targeted by Phishing. Screenshots via Phishlabs.com
Based on the reports conducted by Phishlab industries often targeted by Phishers are Email/Online services followed by financial, Payment services, and even cloud storage.
5. Worms

Most Famous and first Worm created. Morris worm image
What is a Computer worm?
A computer worm is a type of malware designed to replicate itself and spread autonomously across computer networks. Unlike viruses, worms do not require a host file to attach to, as they are standalone programs capable of self-replication. Worms leverage network connections to move from one device to another, often exploiting vulnerabilities in software or operating systems.
Once a computer is infected with a worm, the worm can independently copy itself and distribute copies to other connected devices. Worms can spread rapidly, and their ability to propagate autonomously makes them a potent threat in networked environments.
Worms may be designed for various purposes, including data theft, disruption of network services, or even creating networks of compromised computers, known as botnets, for use in other malicious activities. To mitigate the risk of worm infections, it’s crucial to maintain up-to-date security measures, including regular software updates and the use of firewalls and antivirus software.
A Basic History Of Worm
The history of computer worms dates back to 1988 when a computer science student at Harvard University, Robert Tappan Morris, created what is now famously known as the Morris Worm. Morris intended the self-replicating program to be a benign tool to gauge the size of the internet. However, a miscalculation in the worm’s design caused it to replicate more rapidly than intended, leading to unintended consequences.
The Morris Worm quickly spread across the internet, infecting thousands of computers. Instead of just measuring the size of the internet, it caused a widespread Denial of Service (DDoS) due to its rapid replication and consumption of system resources. The worm’s impact was significant, highlighting the potential dangers of self-replicating malware and the need for improved cybersecurity measures.
The Morris Worm incident played a crucial role in shaping the field of computer security, leading to increased awareness, research, and the development of countermeasures to combat the growing threat of malicious worms and other forms of malware.
Worm Effects On a Device/Computer
- Slow performance of infected computer
- Often crashed
- Flooding the archive with junk files
- Can be used to create a botnet or zombie network
- Delete files
- Open a backdoor
- Infects a single computer multiple times
How Can you get Infected by Worm Malware?
You can get infected by worm malware through various means, showcasing the versatility of this type of threat:
- File-sharing networks: Worms can exploit file-sharing networks, infecting files in shared directories and spreading to other connected computers or devices.
- Emails: Worms can be transmitted through emails, similar to the infamous I LOVE YOU Trojan that infected millions of Windows computers.
- Social networks: Social networks are susceptible to worm infections, as seen in the case of MySpace, which was impacted by the Sammy Worm.
- Software vulnerabilities: Worms can exploit software vulnerabilities or security holes, as exemplified by the Morris Worm, which detected and exploited weaknesses in software.
- Infected sites: Malicious websites, often controlled by hackers, can host a variety of malware, including worms.
- External devices: Worms can spread through infected external hardware such as USB sticks, SD cards, or even the memory of phones.
- Messengers: Similar to emails, worms can infect messengers and spread through text messages.
Worms, being one of the earliest and most effective forms of malware, continue to pose a threat to devices connected to the internet. It’s essential to stay vigilant, keep software up-to-date, and employ robust cybersecurity measures to prevent worm infections and other malware threats.
6. Virus

You may be familiar with the flu virus right? The flu virus can spread from one infected person to another. In computing a virus was a program designed to replicate and spread itself from one device to another, it uses an infected file as a host to spread itself to other victims.
Basic History Of Computer Virus
The history of computer viruses dates back to 1986 when the first known computer virus named “Brain” was created. However, there seems to be a slight discrepancy in the details you provided. The Brain virus was not created in the 1960s; it was actually developed in 1986 by two Pakistani brothers, Amjad Farooq Alvi and Basit Farooq Ali.
The Brain virus was a boot sector virus that infected MS-DOS systems. The motivation behind creating the virus was different from what you mentioned.
The brothers did not intend to teach a lesson to software pirates. Instead, they created the virus to protect their medical software business.
The Brain virus included the brothers’ contact information and a message informing users that their machines were infected. The idea was to trace and identify users who were using pirated copies of their software.
However, the unexpected spread of the Brain virus globally highlighted the unintended consequences of creating such programs.
The virus became one of the earliest instances of unintended global malware propagation, affecting computers in the United States, the United Kingdom, and various other parts of the world.
This incident marked the beginning of the evolving landscape of computer viruses and the need for cybersecurity measures to counteract their unintended spread.
How Can You Get Infected by Computer Virus?
Getting infected by a computer virus can happen through various means, emphasizing the importance of maintaining cybersecurity practices:
- USB Stick: Flash drives or USB sticks can inadvertently transfer viruses to your computer. These devices may carry viruses unnoticed and potentially infect other computers when connected.
- Malicious Websites: Visiting certain websites, especially those associated with explicit content or from the dark and deep web, can expose your computer to various forms of malware, including viruses.
- Unsecured Downloads: Torrent sites, known for hosting a range of content, have been reported to contain malware, including viruses. Downloading files from these unsecured sources increases the risk of malware infection.
- Pirated Software/Cracked Software: Using pirated or cracked software obtained from unofficial sources poses a significant risk. Such software may contain hidden malware or viruses that can compromise your device’s security, slow down its performance, or even spy on your activities.
To mitigate the risk of virus infections, it is crucial to adopt good cybersecurity practices. These include using reputable antivirus software, keeping software and operating systems up-to-date, avoiding suspicious websites, and refraining from downloading or using unauthorized and pirated software. Regularly scanning external devices like USB sticks for potential threats is also advisable.
What Are the Effects of Computer Virus On Your Device?
- Slows down device/computer
- Delete files
- Modify files
- Steal information
- Record keystroke
A virus is one of the oldest and most popular kinds of malware but still has a potential threat even today.
7. Spyware

What Is a Spyware?
Spyware is a form of malware or cyber threat specifically designed to spy on its victims. Cybercriminals employ spyware as a tool for initial reconnaissance, gaining insight into the activities and information of the targeted user. The information collected is often used to prepare for subsequent attacks, such as ransomware or identity theft.
This type of malware can clandestinely attach itself to a device or computer, discreetly recording and monitoring various activities. Spyware is capable of capturing a wide range of sensitive information, including browser history, login credentials, passwords, bank account details, and other personally identifiable information.
The goal is to gather intelligence on the victim for nefarious purposes, such as financial fraud, identity theft, or launching more targeted and damaging cyber attacks.
Protecting against spyware involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including the use of reputable antivirus and anti-spyware software, regularly updating security protocols, and being cautious about downloading files or clicking on links from untrusted sources.
What Are The Harmful Effects of Spyware?
- Spyware can use your computer resources and slows down or often crash your computer.
- It can be used to send some other malware on your computer like ransomware.
- Steal some important information like browser history, passwords, usernames, and other valuable information.
- Records all your internet activity
How can you get Infected by Spyware?
- From Worms, viruses, Trojans
- Untrusted website
- Unsecured Download
- Pirated software
- Torrent Download
- Deepweb/Darkweb
- Fake download links
- Unknown email
- Messenger
- Adware
Spyware was designed for stealth and is hard to detect and often disguised as a legitimate app, spyware is every ware from email, software, and pop-ups. so beware of spyware!
Related Article: Best Antivirus for Android
Bottom line
In conclusion, the landscape of online threats encompasses various forms, including data breaches, malware, and exploits. Our best defense against these threats lies in cultivating threat awareness and knowledge. This understanding prompted an in-depth exploration of potential internet safety threats to empower users with information.
To bolster our defenses, the adoption of reliable safety tools such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), anti-malware software, and firewalls is essential. These tools play a crucial role in providing enhanced protection for our devices, safeguarding against a range of cyber threats.
A fundamental principle in the realm of internet safety is the mantra “think before you click.” Practicing caution, avoiding suspicious links, and being discerning about online interactions are paramount.
By combining threat awareness, knowledge, and the proactive use of safety tools, individuals can significantly strengthen their defenses against the ever-evolving landscape of online threats. Internet safety is a shared responsibility, and staying informed and vigilant is key to navigating the digital world securely.
Credits to our great sources: Malwarebytes labs, Kaspersky labs, Bitdefender labs, Sophos Labs, McAfee Labs, IBM X-Force Threats reports, Datto.com, Verizon Data breach reports, Symantec Research Labs, Breachlevelindex.com.


